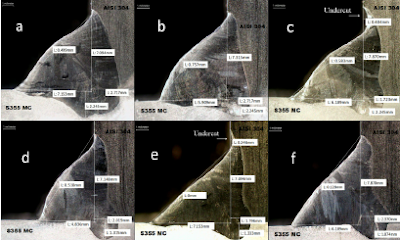
MACRO SECTION
Object: To examine a cross section of a weld for internal defects and soundness.
Method: A transverse section of the weld is cut out. The cross section is then visually inspected. The section is filed down from rough to smooth, then emery or wet/dry papered down to a surface finish of 600 grit. The surface is then etched in NITAL (5% - 10% nitric acid in alcohol), washed off, rinsed and dried. (Possibly a final clean with acetone and mount in Bakelite) The specimen is then inspected at up to 10-x magnification.
Reporting Results:
- Material.
- Welding process.
- Specimen identification.
- Sentencing standard.
- Thickness.
- Geometric flaws - type, size and location.
- Internal flaws - type, size and location.
- Parent metal flaws - type, size and location.
- Accept or reject, to standard, for each flaw.
Comparison of macro section and micro section:
MACRO MICRO
Magnification x 10 x 1000
Finish 600 grit 1 micron (high level polish)
Features/ defects cracks, slag, LOF, etc. inter granular structure
Uses procedure/welder qualification research/failure analysis