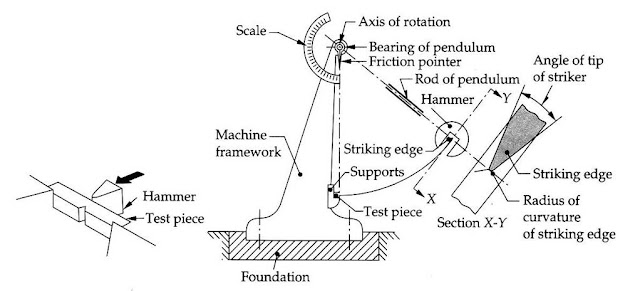
CHARPY V NOTCH IMPACT TEST
Object: To determine the amount of energy absorbed in fracturing a standardized test piece at a specified temperature.
Method: A machined, notched specimen is broken by one blow from a pendulum. Because scatter occurs in the results, at least three specimens are used to assess the joint represented. Testing is carried out at a temperature specified in the appropriate application standard.